Introduction to Advancements in Orthopedic Medicine
Orthopedic medicine has undergone significant evolution over the years, transitioning from traditional methods to innovative technologies that enhance patient care and treatment effectiveness. Historically, orthopedic interventions predominantly involved invasive surgical techniques, often leading to prolonged recovery times and considerable pain. However, recent advancements have transformed the landscape, introducing minimally invasive procedures, robotic-assisted surgeries, and enhanced imaging modalities that facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The significance of these new technologies in orthopedic treatments cannot be overstated. They not only enable healthcare professionals to address common orthopedic issues—such as fractures, joint pain, and degenerative diseases—more effectively but also improve overall patient safety and satisfaction. For instance, techniques like arthroscopy allow surgeons to diagnose and treat joint problems with small incisions, leading to less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and shorter recovery periods.
As the prevalence of orthopedic conditions continues to rise due to factors such as aging populations and increased physical activities, the demand for innovative solutions has become more pressing. The healthcare community recognizes the necessity for advancements that improve surgical precision, optimize rehabilitation processes, and ultimately enhance patient outcomes. Technologies such as 3D printing and advanced prosthetics have emerged, providing personalized solutions tailored to the specific anatomical needs of patients.
This section sets the foundation for a comprehensive exploration of how these technological advancements are reshaping orthopedic practices. By focusing on patient safety and recovery, modern orthopedic treatments are not only addressing existing challenges but are also paving the way for a future where orthopedic care is more effective, efficient, and patient-centered. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into the specific technologies that are driving this transformation in orthopedic medicine.

Robotic-Assisted Surgery: A New Era in Orthopedics
Robotic-assisted surgery represents a remarkable advancement in the field of orthopedics, leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance surgical precision and patient outcomes. At its core, this innovative approach integrates advanced robotic systems with traditional surgical methods, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy. These systems are equipped with high-definition cameras and robotic arms that translate a surgeon’s hand movements into highly precise actions within the patient’s body, thereby minimizing the margin for error.
One of the primary advantages of robotic-assisted surgery is its ability to enhance precision. Traditional orthopedic surgeries often involve extensive manual manipulation, which can lead to variations in technique and potential complications. In contrast, robotic systems allow for meticulous movements, ultimately resulting in better alignment of joints, more precise placements of implants, and fewer errors during surgical procedures. This increased accuracy can significantly reduce the likelihood of revision surgeries, which are often necessary due to initial complications.
Moreover, robotic-assisted procedures typically lead to reduced recovery times for patients. Since these surgeries are often less invasive than their traditional counterparts, patients experience less trauma to surrounding tissues. This can result in less postoperative pain and quicker rehabilitation. A multitude of studies supports these claims, indicating that patients who undergo robotic-assisted orthopedic surgeries often return to their daily activities more rapidly compared to those who have had conventional surgeries.
Statistical evidence further underscores the effectiveness of robotic-assisted surgery. A recent study indicated that hospitals employing robotic systems for orthopedic surgeries reported a reduction in complication rates by over 30%. Additionally, patients benefitting from these robotic interventions experienced shorter hospital stays, averaging around two days, as opposed to the longer recoveries typically seen with traditional surgeries. The integration of robotic technology in orthopedic practice not only promotes better patient outcomes but also signifies a transformative shift in surgical methodologies.
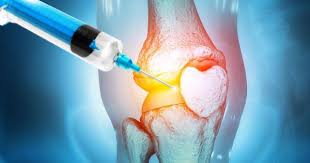
Understanding PRP Therapy for Joint Pain
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is an innovative treatment option that is gaining traction in the orthopedic field, particularly for managing joint pain. This technique uses a patient’s own blood, which is drawn and processed to concentrate the platelets and growth factors that facilitate tissue regeneration. The fundamental premise behind PRP therapy is simple: by injecting this concentrated solution directly into the affected joint, it is believed that healing can be significantly accelerated, providing relief from pain and improving function.
The mechanism of action for PRP therapy centers on the growth factors contained within the platelets. These factors play a critical role in the healing process by promoting cellular repair, reducing inflammation, and stimulating new tissue formation. This healing process is especially beneficial for individuals suffering from conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and sports-related injuries. Current research indicates that PRP therapy can lead to substantial pain relief and improve joint function, making it a valuable option for patients who have not achieved satisfactory results from conventional treatments.
Clinical studies have shown promising outcomes for various joint issues, highlighting the versatility of PRP therapy. For instance, athletes have reported significant recovery improvements following PRP injections, allowing them to return to their activities sooner and with greater efficiency. Additionally, numerous patient testimonials affirm that PRP therapy has enhanced their quality of life, particularly in the realm of alleviating chronic joint pain that has not responded to other forms of treatment.
As technology and research in orthopedic medicine evolves, the adoption of PRP therapy continues to expand, particularly within sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professionals are increasingly recognizing its potential, leading to ongoing investigations and clinical trials, which aim to further understand its efficacy and optimize treatment protocols. Overall, PRP therapy stands out as a promising advancement in the management of joint pain, harnessing the body’s own healing capabilities for effective recovery.
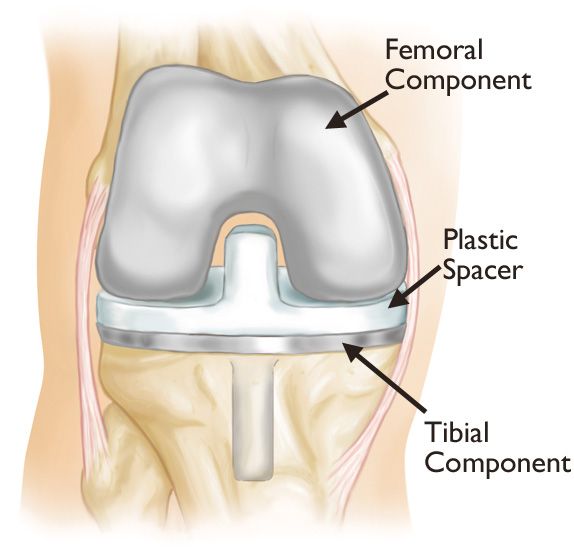
Minimally Invasive Joint Replacement Techniques
Minimally invasive joint replacement techniques represent a significant advancement in orthopedic surgery, providing numerous benefits over traditional methods. These innovative approaches focus on reducing trauma to surrounding tissues, which can lead to greater patient satisfaction and enhanced recovery experiences. During minimally invasive procedures, smaller incisions are employed, resulting in less bleeding and a lower risk of infection, contributing to a more favorable postoperative outcome.
One of the primary advantages of minimally invasive joint replacement is the reduction in hospital stays. Many patients undergoing these advanced procedures can expect to be discharged within a few days, compared to the longer recovery periods associated with conventional surgeries. Shorter hospital stays not only benefit patients by enabling quicker returns to daily activities but also help to alleviate the burden on healthcare facilities.
Another distinction of minimally invasive techniques is the accelerated recovery times. Patients often experience less pain and swelling, allowing for more efficient rehabilitation. The quicker recovery is particularly advantageous for older adults and those with active lifestyles, as it allows them to resume their normal activities sooner. Various approaches to minimally invasive joint replacement, such as the direct anterior approach for hip replacement or the subvastus approach for knee replacement, are tailored for specific joint conditions. Each technique has its particular indications, with certain approaches being more suitable for patients with specific anatomical considerations or overall health profiles.
Patient eligibility for these innovative techniques is an essential factor to consider. While many patients can benefit from minimally invasive interventions, factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of the joint condition play crucial roles in determining whether a patient is a suitable candidate. Success rates for minimally invasive joint replacement surgeries have been promising, with many studies indicating comparable or improved outcomes when set against traditional surgical techniques, highlighting the evolving landscape of orthopedic treatment options.
Regenerative Medicine: Healing from Within
Regenerative medicine represents a groundbreaking approach in orthopedic treatments, focusing on harnessing the body’s natural healing processes to restore function and improve patient outcomes. This medical field utilizes innovative therapies such as stem cell therapy and tissue engineering to promote healing in damaged tissues and joints, offering a promising alternative to traditional surgical interventions or long-term medication.
Stem cell therapy, a key component of regenerative medicine, involves the use of stem cells—undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various specialized cell types. These cells can be harvested from the patient’s own body, typically from adipose tissue or bone marrow, minimizing the risk of rejection and complications. Once introduced into the injured area, stem cells can differentiate into specialized cells needed for repair, facilitating recovery from degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis and tendon injuries. This therapy holds great potential as it aims not just to alleviate symptoms, but to regenerate damaged tissues and restore normal function.
Additionally, tissue engineering plays a critical role in regenerative medicine by utilizing scaffolds, biomaterials, and growth factors to create structures that can support cell attachment and growth. This technique can be particularly beneficial for patients with significant tissue loss or damage, providing a framework for new tissue to form. With advancements in technology, such as 3D printing, the customization of scaffolds tailored to individual patients’ needs is becoming increasingly accessible.
As these regenerative therapies continue to be integrated into existing orthopedic practices, the future of orthopedic treatments looks promising. Research is ongoing to better understand the mechanisms involved in these therapies and to optimize their applications in regenerative medicine. This innovative branch of medicine is poised to revolutionize the treatment landscape, offering patients a chance for more effective and less invasive solutions to their orthopedic challenges.

The Role of Technology in Patient Care and Recovery
The integration of technology into orthopedic treatments has substantially transformed patient care and recovery processes. Digital tools have emerged as pivotal components in enhancing patient engagement, monitoring recovery metrics, and facilitating efficient communication between healthcare providers and patients. One prominent advancement is the utilization of telemedicine, which has revolutionized the way patients access consultations and follow-up appointments. This technology allows patients to connect with orthopedic specialists regardless of their geographical location, thereby increasing access to care and minimizing travel-related stress.
In addition to telemedicine, wearable devices have gained popularity in orthopedic health management. These devices, which include smartwatches and fitness trackers, enable real-time monitoring of recovery metrics such as mobility, physical activity levels, and compliance with prescribed rehabilitation exercises. By collecting and analyzing data, healthcare providers can assess patients’ progress more accurately and provide tailored advice that suits individual recovery needs. This not only ensures a more personalized treatment approach but also keeps patients motivated and engaged throughout their rehabilitation journey.
Another significant aspect of technology in orthopedic care is the implementation of patient education platforms. These digital solutions deliver vital information about recovery protocols, pain management techniques, and exercise regimens directly to patients’ devices. By equipping patients with knowledge, these platforms foster a greater understanding of their conditions and enhance their ability to participate actively in their recovery. Such engagement is crucial, as studies have shown that informed patients are more likely to adhere to their treatment plans and experience better outcomes.
Overall, the role of technology in orthopedic patient care not only streamlines communication but also empowers patients by providing them with the tools and resources needed to navigate their recovery effectively. Through its multifaceted applications, technology continues to shape the future of orthopedic treatments, highlighting its significance in enhancing patient care and recovery.More advancements in this field are anticipated, promising an even more profound impact on patient outcomes.

Challenges and Considerations in Advanced Orthopedic Treatments
The incorporation of advanced technologies in orthopedic treatments offers substantial benefits, yet it is accompanied by specific challenges that healthcare providers must navigate. One significant consideration is the requisite training for orthopedic surgeons and their teams. As new technologies, such as robotic-assisted surgeries and 3D printing, are introduced, surgeons must undergo extensive training to ensure they are proficient in utilizing these tools. This demand for education can be time-consuming and costly, often requiring ongoing professional development to remain current with evolving innovations.
Another critical factor is the financial implications associated with employing advanced orthopedic technologies. The initial investments in cutting-edge equipment, along with the maintenance and potential upgrades, can be prohibitively expensive. As healthcare systems strive to balance budgets while improving patient outcomes, these costs may present a barrier to adopting new methodologies. Additionally, insurance coverage for advanced treatments may vary, complicating access for some patients and potentially leading to disparities in treatment availability.
Patient acceptance is also paramount when implementing advanced orthopedic treatments. Some individuals may be hesitant to embrace new technologies, favoring traditional surgical methods due to fear of the unknown or lack of understanding about the benefits offered by modern approaches. Effective communication and education initiatives are crucial for addressing these concerns, ensuring patients fully comprehend the potential advantages, including reduced recovery times and enhanced surgical precision.
Finally, ethical considerations must be addressed in the context of advanced orthopedic treatments. Topics such as informed consent, data privacy, and equitable access to innovative technologies require ongoing dialogue among healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers. Navigating these challenges is essential for the successful integration of advanced technologies in orthopedic care.

The Future of Orthopedic Medicine: Trends and Predictions
As we look ahead, the future of orthopedic medicine is poised for significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology and evolving treatment paradigms. One of the most promising trends is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic conditions. Machine learning algorithms will enhance the accuracy of imaging techniques, allowing for earlier detection of conditions such as osteoporosis and fractures. Moreover, AI can assist in creating personalized treatment plans by analyzing vast amounts of patient data, leading to improved outcomes and reduced recovery times.
Another major trend is the rise of minimally invasive procedures, facilitated by innovative surgical technologies. The development of robotic-assisted surgeries is enhancing precision and reducing the risks associated with traditional orthopedic surgeries. These advancements can offer patients quicker recovery periods and less post-operative pain, significantly improving their overall experience. Additionally, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are expected to play crucial roles in surgical planning and training, helping surgeons visualize complex procedures and enhance their skills.
Personalized medicine is set to reshape orthopedic care by tailoring interventions based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup and lifestyle factors. As research progresses in this area, orthopedic treatment plans may become increasingly specific, optimizing the efficacy of therapies such as regenerative medicine and cellular therapies. Nanotechnology, too, is on the horizon, with the potential to develop next-generation implants and biomaterials that promote healing and integration with the body.
Research and development, coupled with a commitment to adaptation within the orthopedic field, will be vital for harnessing these advancements. Ongoing clinical trials and studies will continue to inform practices, ensuring that orthopedic medicine evolves to meet the needs of patients effectively. As these trends come to fruition, the future holds great promise for enhanced orthopedic care and improved patient outcomes.
FAQs about New Technologies in Orthopedic Treatments
As advancements in orthopedic treatments continue to evolve, patients often have numerous questions regarding these new technologies. Below are some frequently asked questions that aim to clarify common concerns.
1. Are new orthopedic treatment technologies safe?
Many new technologies such as robotic surgery, minimally invasive techniques, and regenerative medicine have undergone extensive testing and clinical trials. Regulatory bodies like the FDA meticulously evaluate these advancements to ensure their safety and efficacy before they are made available to the public. However, it is always advisable for patients to discuss the risks and benefits with their orthopedic specialists.
2. What can I expect during the recovery process?
Recovery timelines can vary based on the specific technology used, the type of procedure performed, and individual patient factors. Minimally invasive procedures typically result in shorter recovery times compared to traditional surgeries. Patients are encouraged to follow their orthopedic surgeon’s recommendations and participate actively in rehabilitation to optimize recovery outcomes.
3. Will my insurance cover advanced orthopedic treatments?
Insurance coverage for new technologies in orthopedic treatments can vary significantly by provider and policy. Patients should contact their insurance company for detailed information on coverage options. Additionally, many orthopedic practices offer financial counseling to help patients navigate the complexities of insurance benefits related to advanced treatments.
4. How can I find qualified orthopedic specialists for new technologies?
Patients seeking orthopedic specialists experienced in the latest technologies should consider several factors. Recommendations from primary care physicians, patient testimonials, and consultations with potential specialists can provide insight into their expertise. Furthermore, many hospitals and clinics have specific departments dedicated to advanced orthopedic care, which can assist patients in making informed choices.
These FAQs demonstrate the emphasis on safety, recovery, insurance coverage, and finding qualified practitioners in the continually evolving landscape of orthopedic treatments. By addressing these concerns, patients can gain comfort in exploring new treatment options available to them.