Introduction to Orthopaedic Robotic Surgery
Orthopaedic robotic surgery represents a significant leap forward in the medical field, offering enhanced precision and outcomes for patients. This advanced surgical method leverages robotic systems and navigation techniques, which have been progressively developed over the past few decades. The concept of integrating robotics into surgery arose in the late 20th century, with initial applications focusing on enhancing the accuracy of procedures that demanded meticulous execution.
The evolution of orthopaedic robotic surgery has been driven by technological advancements, including the development of sophisticated robotic systems and improved imaging techniques. These innovations have enabled surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision, reducing the risk of human error and improving patient recovery times. The integration of robotics into orthopaedic surgery allows for minimally invasive techniques, which are less traumatic for patients and often result in shorter hospital stays and quicker returns to normal activities.
As the medical field continues to embrace technology, the role of robotics in orthopaedic surgery is becoming increasingly important. Robotic systems and navigation techniques enhance the surgeon’s capabilities, allowing for more accurate alignment and placement of implants, which is crucial in procedures such as joint replacements. The ability of these systems to provide real-time feedback and adjust to the surgeon’s movements ensures a higher level of control and precision.
The growing importance of robotics in orthopaedic surgery cannot be overstated. As the population ages and the demand for joint replacement surgeries increases, the need for precise, efficient, and minimally invasive surgical options becomes more critical. Orthopaedic robotic surgery addresses these needs, offering a glimpse into the future of medical procedures where technology and human expertise combine to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
What is Orthopaedic Robotic Surgery?
Orthopaedic robotic surgery represents a significant advancement in the field of orthopaedics, leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance surgical outcomes. At its core, this innovative approach integrates robotic systems and navigation techniques to assist surgeons in performing intricate procedures with unparalleled precision and control. Unlike traditional methods, robotic surgery involves the use of computer-controlled instruments that are guided by the surgeon, who manipulates the robotic arms from a console. This setup allows for highly accurate movements, reducing the margin for human error and improving the overall success rates of the surgeries.
The robotic revolution in orthopaedics has paved the way for a variety of procedures, with knee and hip replacements being among the most common. In these surgeries, the robotic system helps in preoperative planning by creating a 3D model of the patient’s anatomy. This model is used to guide the surgeon during the operation, ensuring optimal alignment and placement of implants. The precision and consistency offered by robotic systems can lead to better joint function, faster recovery times, and reduced postoperative pain for patients.
Another significant advantage of orthopaedic robotic surgery is its minimally invasive nature. The enhanced dexterity of robotic instruments allows for smaller incisions compared to traditional surgery. This means less tissue damage, lower risk of infection, and quicker healing times. Furthermore, the use of robotic assistance can result in more predictable surgical outcomes, which is particularly beneficial for complex cases where traditional techniques might fall short.
In conclusion, orthopaedic robotic surgery embodies the future of surgical care, combining technological innovation with medical expertise to improve patient outcomes. By incorporating robotic systems and navigation techniques, surgeons are empowered to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and efficiency, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for patients undergoing orthopaedic surgeries.
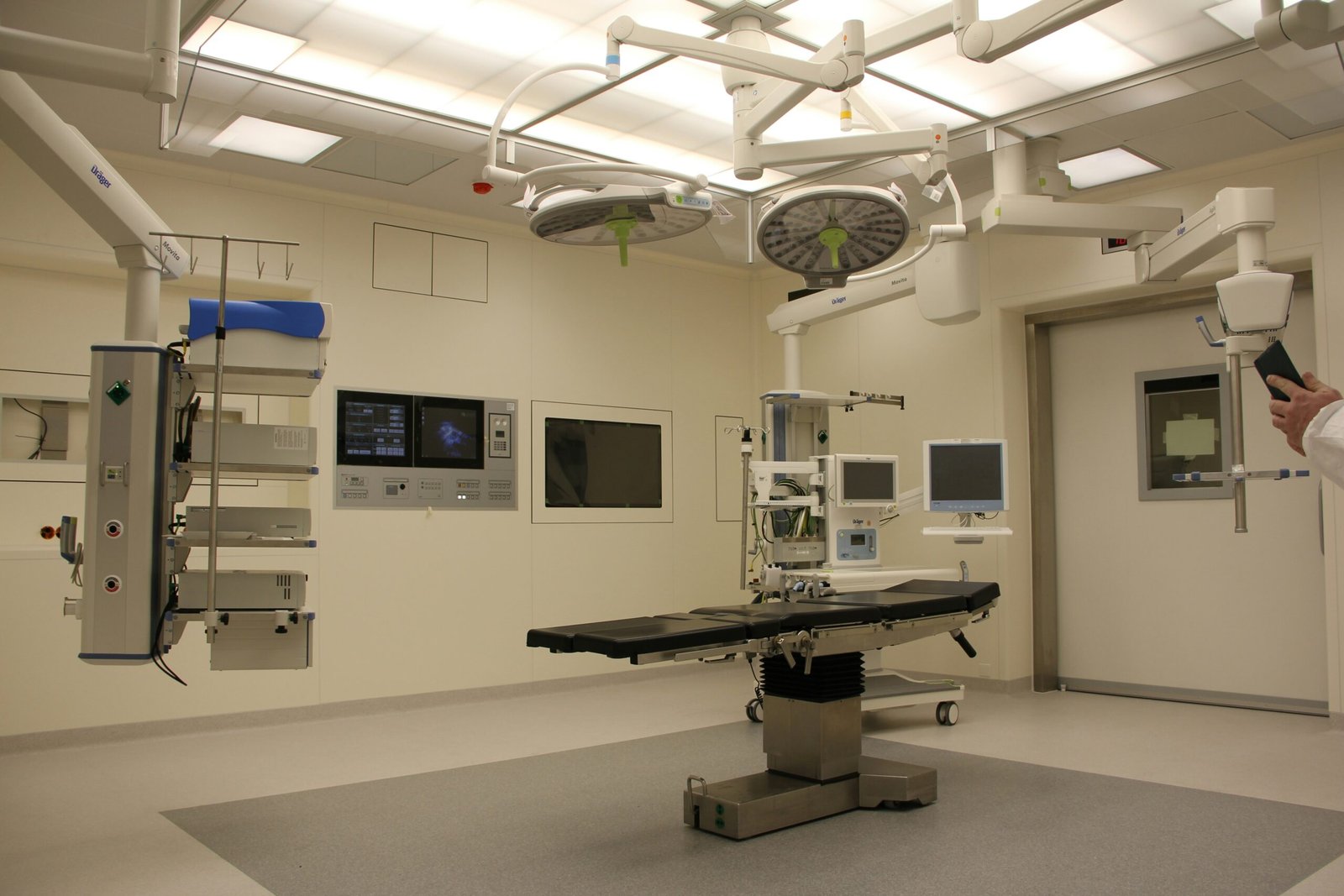
The Technology Behind Robotic Surgery
Advancements in orthopedic robotic surgery are revolutionizing the field by integrating various high-tech components to enhance surgical precision and efficacy. Central to this innovation are the robotic arms, which are meticulously designed to replicate the dexterity and range of motion of a human hand. These robotic arms are equipped with sensors and actuators that allow for precise movements, significantly reducing the margin for human error during surgical procedures.
A crucial element of these systems is the computer interface, which serves as a bridge between the surgeon and the robotic mechanism. This interface is often a sophisticated software platform that enables the surgeon to plan the procedure meticulously before execution. By using preoperative imaging data, the surgeon can map out the surgical site in three dimensions, allowing for detailed planning and simulation. This preoperative planning is especially beneficial in complex orthopedic surgeries, where accuracy is paramount.
Imaging technologies, such as CT scans and MRI, are integral to the success of robotic surgery. These imaging modalities provide real-time, high-resolution views of the surgical site, enabling the robotic system to make precise cuts and adjustments. During the operation, the imaging data is continuously updated and fed into the computer interface, which then guides the robotic arms with pinpoint accuracy. This dynamic interaction between imaging technologies and robotic components is what sets robotic surgery apart from traditional methods.
One of the most significant advantages of using robotic systems and navigation techniques in orthopedics is the enhancement of surgical outcomes. By integrating these sophisticated technologies, surgeons can achieve greater precision, which translates to fewer complications and faster recovery times for patients. Moreover, the minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery often results in smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and decreased postoperative pain.
Overall, the synergy between robotic arms, computer interfaces, and advanced imaging technologies is propelling orthopedic surgery into a new era. These combined technologies not only enhance the surgeon’s capabilities but also improve patient outcomes, making orthopedic robotic surgery a promising frontier in medical science.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery in Orthopaedics
Robotic systems and navigation techniques in orthopaedics represent a significant advancement in the field, offering numerous benefits to both patients and practitioners. One of the primary advantages is the increased accuracy that robotic systems provide. Traditional surgical methods rely heavily on the surgeon’s skill and experience, but robotic systems utilize precise, computer-assisted movements that reduce the margin for error. This heightened precision is particularly beneficial in orthopaedic procedures, where the placement of implants and alignment of bones are critical to the success of the surgery.
Another significant benefit is the reduced trauma to surrounding tissues. Conventional surgical techniques often require large incisions, which can lead to more substantial tissue damage and longer recovery times. In contrast, robotic surgery often involves minimally invasive procedures, with smaller incisions that cause less disruption to the body’s structures. This minimally invasive approach results in less postoperative pain, decreased blood loss, and a lower risk of infection.
Shorter recovery times are another advantage of robotic orthopaedic surgery. Because the procedures are less invasive and more precise, patients typically experience quicker recovery periods. This means that they can return to their normal activities and daily routines much sooner than with traditional surgical methods. Clinical studies have shown that patients who undergo robotic-assisted surgeries tend to have shorter hospital stays and a faster return to physical function.
Improved long-term outcomes are also a notable benefit. The enhanced accuracy and precision of robotic systems lead to better alignment and placement of implants, which can result in longer-lasting surgical results. This is particularly important in orthopaedic surgeries, where the longevity of joint replacements and other implants is crucial to the patient’s quality of life. Patient testimonials frequently highlight the improved mobility and reduced pain they experience following robotic-assisted procedures, underscoring the positive impact on long-term health outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the significant advancements brought about by the robotic revolution in orthopaedic surgery, the technology is not without its challenges. One of the primary limitations is the high cost associated with robotic systems and navigation techniques in orthopedics. The initial investment for acquiring robotic surgical systems can be substantial, and the ongoing maintenance and operational costs add to the financial burden on healthcare facilities. This can make it difficult for smaller hospitals and clinics to adopt these advanced technologies.
Another challenge lies in the need for specialized training. Orthopaedic surgeons must undergo extensive training to effectively utilize robotic systems. This training period can be lengthy and demanding, requiring surgeons to adapt to new methodologies and tools. As a result, there is a learning curve that can temporarily impact surgical efficiency and outcomes. Additionally, the availability of training programs and experienced trainers can be limited, further complicating the widespread adoption of robotic surgery.
Technical malfunctions present another area of concern. While robotic systems are designed to enhance precision and reduce human error, they are not immune to technical issues. Hardware and software malfunctions can occur, potentially leading to delays or complications during surgery. The reliance on advanced technology also means that any technical failure necessitates immediate troubleshooting and repair, which can disrupt surgical schedules and pose risks to patient safety.
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges. Researchers are working on reducing the costs associated with robotic systems by developing more affordable and efficient technologies. Efforts are also being made to streamline the training process, making it more accessible and less time-consuming for orthopaedic surgeons. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are being explored to enhance the reliability and functionality of robotic systems, minimizing the risk of technical malfunctions.
In conclusion, while the robotic revolution holds immense promise for the future of orthopaedic surgery, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the existing challenges and limitations. By continuing to invest in research and development, the medical community can work towards overcoming these obstacles and fully realizing the potential of robotic systems in orthopaedics.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Orthopedic robotic surgery has revolutionized the field, offering unprecedented precision and improved patient outcomes. Several compelling case studies illustrate the transformative impact of these advanced robotic systems and navigation techniques in orthopedics. Each story underscores the significant benefits for both patients and surgeons, demonstrating the efficacy of this technology in real-world applications.
One notable case involves a middle-aged patient suffering from severe osteoarthritis in the knee. Traditional surgical approaches posed a high risk of complications due to the patient’s complex medical history. Opting for robotic-assisted knee replacement, the surgeon utilized a sophisticated robotic system to achieve unparalleled accuracy in implant positioning. The patient experienced a significant reduction in post-operative pain and a faster recovery timeline, returning to an active lifestyle much sooner than expected.
Another success story features a young athlete with a torn ACL. Given the athlete’s need for a swift return to competitive sports, the surgical team employed robotic navigation techniques to ensure precise ligament reconstruction. The enhanced visualization and control provided by the robotic system resulted in optimal graft placement and tensioning, leading to a robust recovery. The athlete was able to resume training within months, demonstrating the efficiency and effectiveness of robotic intervention.
A particularly inspiring case study highlights the experience of an elderly patient undergoing hip replacement surgery. Traditional approaches posed significant risks due to the patient’s age and frailty. The integration of robotic systems allowed for minimally invasive techniques, reducing surgical trauma and shortening hospital stays. The patient reported minimal discomfort and regained mobility quickly, significantly enhancing their quality of life.
These case studies exemplify the profound impact of the robotic revolution in orthopedic surgery. They showcase how robotic systems and navigation techniques can significantly improve surgical outcomes, reduce recovery times, and enhance patients’ overall experiences. The continued advancement and adoption of orthopedic robotic surgery promise even more remarkable success stories in the future.
Future Directions and Innovations
The field of orthopedic robotic surgery is poised to undergo significant transformations driven by advancements in technology. One of the most promising trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into robotic systems and navigation techniques. AI has the potential to enhance decision-making processes by providing surgeons with real-time data analysis, predictive modeling, and optimized surgical plans. This could lead to more precise and efficient procedures, reducing recovery times and improving patient outcomes.
Another emerging innovation in orthopedic robotic surgery is the development of more sophisticated robotic systems. These next-generation robots are expected to offer increased dexterity and finer control, allowing for more complex and delicate surgical maneuvers. Enhanced imaging technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and three-dimensional (3D) visualization, are also being integrated into these systems to provide surgeons with a comprehensive view of the surgical site. This could significantly improve the accuracy of implant placements and alignments, further enhancing the success rates of orthopedic surgeries.
Personalized surgical approaches are another exciting prospect in the realm of orthopedic robotic surgery. By leveraging patient-specific data, such as genetic information and biomechanical characteristics, surgeons can tailor surgical plans to meet the unique needs of each patient. This personalized approach could lead to more effective treatments and faster recovery times, as the surgical procedures would be optimized for the individual patient’s anatomy and condition.
Additionally, the continual improvement of robotic systems and navigation techniques in orthopedics has the potential to make these advanced procedures more accessible. As the technology becomes more refined and cost-effective, a broader range of healthcare facilities could implement these systems, democratizing access to high-quality orthopedic care. This could be particularly beneficial in underserved regions where access to specialized surgical expertise is limited.
Overall, the future of orthopedic robotic surgery holds immense promise. With ongoing advancements in AI, robotic technology, and personalized medicine, the field is set to experience a revolution that could transform the landscape of orthopedic care.
Conclusion: Embracing the Robotic Revolution
The advent of orthopedic robotic surgery has marked a significant milestone in the field of medical science, heralding a new era of precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Throughout this blog post, we have explored the multifaceted impact of the robotic revolution in orthopedic surgery, from the enhanced accuracy of robotic systems and navigation techniques to the substantial benefits for both surgeons and patients.
Robotic systems and navigation techniques in orthopedics are not merely trends but represent a fundamental shift toward more reliable and minimally invasive surgical procedures. The integration of advanced technologies has reduced the margin for error, leading to quicker recovery times, less postoperative pain, and overall improved surgical results. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that these systems will become an integral part of standard surgical practice, offering even more refined capabilities and broader applications.
Understanding the implications of these advancements is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. Staying informed about the latest developments in orthopedic robotic surgery can empower individuals to make educated decisions about their healthcare options. For those considering surgery, the potential benefits of robotic-assisted procedures—such as increased precision and better postoperative outcomes—make it a compelling option worth discussing with their medical professionals.
As we stand on the brink of this technological revolution, it is essential to recognize the transformative potential of robotic systems in orthopedics. We encourage our readers to share their thoughts and experiences with orthopedic robotic surgery in the comments below. Your insights can help us all better understand the real-world impact of these groundbreaking advancements and foster a community of informed individuals ready to embrace the future of orthopedic care.
Frequently Asked Question ?
Q. What is robotic orthopaedic surgery?
Ans. Robotic orthopaedic surgery involves using robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing precise and minimally invasive procedures. These systems enhance surgical accuracy and improve patient outcomes.
Q. How does robotic surgery differ from traditional surgery?
Ans. Unlike traditional surgery, which relies solely on the surgeon’s hands, robotic surgery utilizes robotic arms controlled by the surgeon. This allows for greater precision, flexibility, and control during procedures.
Q. What are the benefits of robotic orthopaedic surgery?
Ans. Benefits include reduced blood loss, shorter recovery times, less postoperative pain, smaller incisions, and improved accuracy in procedures such as joint replacements.
Q. What types of procedures can be performed with robotic assistance?
Ans. Robotic systems can assist in various orthopaedic procedures, including knee and hip replacements, spine surgeries, and repairs of fractures and soft tissues.
Q. Is robotic surgery safe?
Ans. Yes, robotic surgery is generally considered safe. It combines the surgeon’s expertise with advanced technology to minimize risks and improve outcomes. However, as with any surgery, there are inherent risks involved.
Q. What training do surgeons undergo to perform robotic surgeries?
Ans. Surgeons typically undergo extensive training in the use of robotic systems, including simulation practice and hands-on experience under the supervision of experienced mentors.
Q. Will insurance cover robotic orthopaedic surgery?
Ans. Coverage varies by insurance provider and policy. Patients should check with their insurance companies to determine what is covered and any out-of-pocket costs.
Q. What is the recovery process like after robotic orthopaedic surgery?
Ans. Recovery varies depending on the procedure performed, but many patients experience less pain and faster recovery times compared to traditional surgery. Physical therapy may be recommended to aid rehabilitation.
Q. Are there any risks or complications associated with robotic surgery?
Ans. While robotic surgery is safe, potential risks include infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. Discussing these risks with your surgeon is essential.
Q. What does the future hold for robotic orthopaedic surgery?
Ans. The future of robotic orthopaedic surgery is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, which may enhance surgical precision and patient outcomes further.







Site
August 9, 2024Very interesting subject, thanks for posting.Raise your business