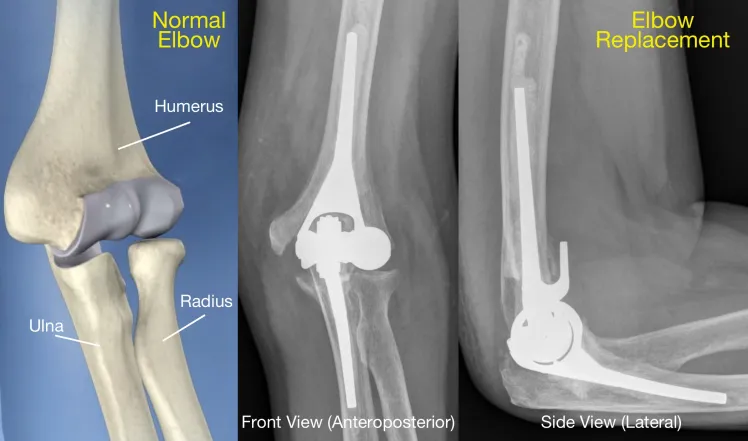
Introduction to Primary Elbow Arthroplasty
Primary elbow arthroplasty, commonly known as elbow replacement surgery, is a significant procedure within the field of orthopedic surgery. This surgical intervention is primarily employed to address severe joint conditions that compromise the elbow’s functionality and cause chronic pain. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and traumatic injuries are leading causes that necessitate primary elbow arthroplasty.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that leads to inflammation of the joint lining, causing pain, swelling, and eventual joint destruction. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is characterized by the degeneration of joint cartilage and underlying bone, leading to stiffness and pain in the elbow. Traumatic injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can also result in significant joint damage that may require surgical intervention.
The primary goals of elbow arthroplasty are to alleviate pain, restore joint function, and enhance the overall quality of life for patients. Pain relief is a crucial outcome, as chronic elbow pain can severely limit daily activities and reduce a patient’s independence. Improved joint function is another essential objective of the surgery, allowing patients to regain a range of motion and perform tasks that were previously hindered by elbow issues. Ultimately, the enhancement of the patient’s quality of life is the overarching goal, enabling individuals to return to their normal routines and enjoy an active lifestyle.
By addressing these debilitating conditions with primary elbow arthroplasty, orthopedic surgeons can provide significant relief and improved outcomes for their patients. This surgical option remains a vital solution for those suffering from severe and chronic elbow conditions, ensuring that patients can achieve pain-free and functional use of their elbows.
Common Problems Associated with Primary Elbow Arthroplasty
Primary elbow arthroplasty, while generally effective in restoring function and relieving pain in patients with severe elbow joint conditions, is not without its complications. One of the most significant challenges associated with this procedure is infection. Studies show that the infection rate following primary elbow arthroplasty ranges from 2% to 10%, with higher rates observed in patients with comorbidities such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis.
Implant loosening is another prevalent issue, often resulting from mechanical wear or biological factors. Research indicates that implant loosening can affect up to 15% of patients, leading to pain and decreased joint function. This problem is exacerbated in younger, more active individuals who place greater demands on the prosthesis.
Joint stiffness is a frequent postoperative complication, occurring in approximately 20% of cases. This stiffness can significantly impair daily activities and overall quality of life. Surgical technique plays a crucial role in minimizing this issue, with meticulous soft tissue handling and appropriate rehabilitation protocols being essential for optimal outcomes.
Nerve injury, though less common, remains a concern, particularly involving the ulnar nerve. The incidence of nerve injury varies, with some studies reporting rates as high as 5%. Such injuries can result in sensory deficits or motor weakness, necessitating further medical intervention.
Periprosthetic fractures are another complication that can occur, especially in patients with osteoporotic bone or those experiencing trauma. These fractures are reported in about 3% to 5% of primary elbow arthroplasty cases and often require complex surgical management.
Patient factors, including age, activity level, and existing comorbidities, significantly influence the likelihood of these complications. Older patients or those with multiple health issues are at a higher risk for adverse outcomes. Similarly, surgical factors such as the choice of implant type and the surgeon’s experience and technique are critical in determining the success of the procedure.
Solutions and Preventative Strategies
Mitigating the problems associated with primary elbow arthroplasty requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing advancements in surgical techniques, enhanced implant designs, and comprehensive postoperative care protocols. One of the foremost strategies involves meticulous preoperative planning. Physicians must evaluate the patient’s medical history, conduct detailed imaging studies, and consider potential complications to tailor the surgical approach effectively. This preparation is crucial in anticipating challenges and optimizing surgical outcomes.
Advancements in surgical techniques have significantly contributed to reducing complications in primary elbow arthroplasty. Minimally invasive procedures, for instance, have been shown to decrease surgical trauma and accelerate recovery times. Surgeons now have access to improved tools and techniques, such as computer-assisted navigation and robotic surgery, which enhance precision and reduce the risk of errors.
Implant design has also seen remarkable improvements. Modern prosthetics are engineered for better fit and function, utilizing biocompatible materials that reduce the risk of rejection and wear. Enhanced materials, such as highly cross-linked polyethylene and advanced metal alloys, have demonstrated increased durability and longevity, thereby reducing the likelihood of revision surgeries.
Postoperative care is another critical aspect of successful primary elbow arthroplasty. Enhanced recovery protocols, including pain management strategies and early mobilization, play a vital role in reducing complications. Comprehensive rehabilitation programs tailored to individual needs promote joint flexibility and strength, improving overall outcomes. Patient education is equally important, ensuring that individuals understand their rehabilitation regimen and the importance of adhering to prescribed exercises and follow-up appointments.
Innovative technologies continue to emerge, showing promise in improving the outcomes of primary elbow arthroplasty. For example, 3D printing is being utilized to create custom implants that fit patients’ unique anatomical structures precisely. Additionally, regenerative medicine, including the use of stem cells and growth factors, is being explored to enhance tissue healing and integration with implants.
By integrating these strategies and leveraging technological advancements, the medical community can effectively address the challenges associated with primary elbow arthroplasty, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Future Directions and Research
Primary elbow arthroplasty is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research and potential developments poised to significantly enhance patient outcomes. One emerging trend is the incorporation of biologics in elbow arthroplasty. Biologics, including growth factors, stem cells, and tissue engineering, hold promise for improving the healing process and potentially reducing the risk of postoperative complications. These advancements could lead to better integration of implants with the native bone and soft tissues, thereby enhancing the longevity and effectiveness of the procedures.
Another significant development is the use of custom implants. Customization allows for implants to be tailored to the specific anatomical needs of individual patients, which can improve the fit and function of the prosthesis. Advances in imaging technologies and computer-aided design have made it feasible to create these bespoke solutions, which are particularly beneficial for patients with unique anatomical challenges or those requiring revision surgeries.
Minimally invasive techniques are also gaining traction in the realm of primary elbow arthroplasty. These approaches aim to reduce surgical trauma, minimize scarring, and expedite recovery times. Techniques such as arthroscopy and smaller incision surgeries are being refined and increasingly incorporated into clinical practice, offering patients less invasive options with potentially quicker return to normal activities.
Current studies and clinical trials are exploring various innovative methods to improve patient outcomes in primary elbow arthroplasty. Research is focusing on enhancing implant materials, developing new surgical techniques, and improving postoperative rehabilitation protocols. For instance, trials are assessing the efficacy of novel biomaterials that may offer superior biocompatibility and durability compared to traditional options.
While the future of elbow arthroplasty appears promising, challenges remain. Ensuring the widespread adoption of new technologies, addressing the high costs associated with custom and biologic implants, and managing the learning curve associated with minimally invasive techniques are significant hurdles. Nevertheless, these challenges bring opportunities for further research, innovation, and collaboration within the field, fostering continued advancements in primary elbow arthroplasty.







Web Page
August 9, 2024Really wonderful info can be found on weblog.Raise your business