Introduction to Orthopedic Surgery Alternatives
Orthopedic surgery is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system. This system includes bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, which play a crucial role in facilitating movement and supporting the body. Common conditions that lead to surgical intervention include osteoarthritis, sports injuries, fractures, and congenital deformities. For many patients, orthopedic surgery represents a pathway to alleviating pain, restoring function, and improving quality of life; however, the decision to pursue surgical intervention can be complex and multifaceted.
In recent years, an increasing number of patients have begun to explore alternatives to traditional orthopedic surgery. There are several reasons for this shift. Firstly, the financial aspect of surgery can be daunting. Orthopedic procedures are often expensive, with costs not only associated with the surgery itself but also with post-operative care, rehabilitation, and potential complications. Many patients find themselves seeking more cost-effective options that may yield similar benefits without the burden of high medical bills.
Moreover, the recovery time following surgery can be extensive, requiring weeks or even months of rehabilitation and physical therapy. This long recuperation period can disrupt daily life, work, and other activities, leading patients to consider non-surgical alternatives that may provide quicker relief and enable them to return to their normal lifestyles more rapidly. Additionally, potential risks associated with surgery, such as infections, complications from anesthesia, and the need for follow-up procedures, further motivate individuals to seek out alternative treatment modalities.
This exploration of orthopedic surgery alternatives includes various non-invasive and less risky options. The intention of this blog post is to provide a comprehensive overview of these options, empowering patients with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions regarding their health and well-being.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Techniques
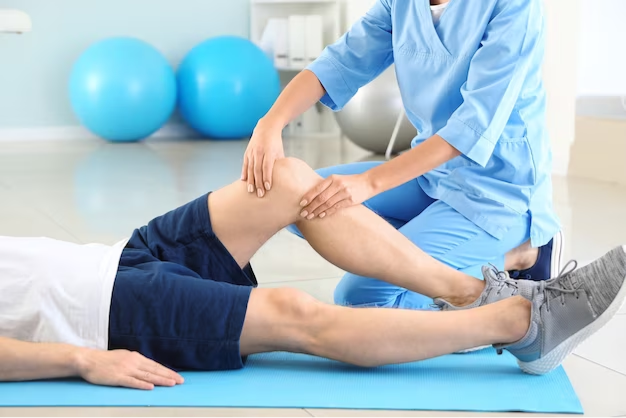
Physical therapy has emerged as a primary alternative to orthopedic surgery for individuals dealing with musculoskeletal issues. This therapeutic approach aims to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and bolster overall strength through a range of carefully designed techniques and exercises. Physical therapists utilize modalities such as manual therapy, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and heat treatments to target problem areas. These techniques can significantly reduce discomfort and promote healing without the need for invasive procedures.
A tailored rehabilitation plan is crucial in addressing the unique needs of each patient. Upon the initial assessment, physical therapists evaluate the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and current physical abilities. Based on this information, they can develop a customized regimen that may include specific exercises aimed at improving flexibility, coordinating movements, and strengthening relevant muscle groups. For instance, patients with knee pain may benefit from exercises focused on quadriceps and hamstring strength, while those suffering from shoulder injuries might perform rotator cuff strengthening routines.
The effectiveness of physical therapy is supported by numerous success stories and research findings. Many patients have reported significant improvements in pain management and functional abilities through dedicated participation in a rehabilitation program. Statistical data indicates that up to 80% of patients notice improved mobility and reduced pain levels after engaging in structured physical therapy. Moreover, studies suggest that early intervention with physical therapy can often help prevent the need for surgical intervention altogether.
In conclusion, physical therapy stands as a viable alternative to orthopedic surgery, presenting varied techniques aimed at pain relief and functional improvement. With careful planning and commitment, patients can achieve remarkable outcomes, fostering a better quality of life free from pain and restrictions.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management is a fundamental aspect of treating musculoskeletal conditions when considering alternatives to orthopedic surgery. A variety of options can alleviate symptoms effectively, enhancing quality of life without invasive intervention. One of the most common approaches is medication, which can range from over-the-counter options such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to prescription medications tailored for more severe discomfort. Opioids, while effective, are recommended as a last resort due to their potential for dependence and side effects.
In addition to oral medications, corticosteroid injections serve as another valuable strategy for pain management. These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly to the site of pain, providing temporary relief from acute flare-ups associated with conditions like arthritis or tendonitis. This targeted treatment can significantly reduce inflammation and, consequently, pain, allowing patients to engage in rehabilitation and physical therapy more effectively.
Alternative therapies have also gained traction among those seeking to avoid surgery. Acupuncture, for instance, is an ancient Chinese practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. Numerous studies indicate that acupuncture can relieve pain through stimulating the body’s natural painkillers and promoting blood flow to affected areas.
Chiropractic care offers another non-invasive avenue for pain relief. By focusing on spinal alignment and joint manipulation, chiropractors aim to alleviate pain and improve function. This holistic approach emphasizes the body’s ability to heal itself and can be particularly beneficial in treating back and neck pain.
Ultimately, exploring these pain management strategies can provide significant benefits for individuals seeking to avoid orthopedic surgery. By integrating a combination of medication, injections, acupuncture, and chiropractic care, patients often find relief that enhances their daily function and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
Exploring alternative approaches to orthopedic issues, lifestyle modifications and home remedies play a pivotal role in managing chronic conditions and possibly avoiding orthopedic surgery. One significant aspect of these modifications is weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints, particularly in weight-bearing regions such as the knees and hips. Individuals can achieve effective weight management through balanced nutrition and appropriate calorie intake, which ensures that they do not exacerbate existing orthopedic issues.
In addition to weight control, dietary choices can also influence musculoskeletal health. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and essential vitamins can support joint function and overall well-being. Foods such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables are beneficial choices that can alleviate inflammation and enhance recovery.
Regular exercise, tailored to individual capabilities, is equally important in promoting orthopedic health. Low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, and yoga can improve flexibility, strengthen muscles around joints, and alleviate stiffness. Physical activity, when performed consistently, contributes to the overall stability and mobility of the musculoskeletal system, aiding in the prevention of injuries and the management of pain.
Ergonomic adaptations within one’s workspace or home can also facilitate better posture and reduce undue stress on the body. Simple changes, such as using chairs that support spinal alignment or arranging workstations to minimize repetitive strain, can create a healthier environment conducive to recovery.
Lastly, home remedies such as hot and cold therapy, gentle stretching, and the use of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can provide symptomatic relief. However, consulting with healthcare professionals before initiating any home remedy is advisable to ensure its appropriateness for specific conditions. These lifestyle modifications emphasize a long-term commitment to health improvement and can significantly enhance quality of life while decreasing the likelihood of orthopedic surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions?
1. What are the common alternatives to orthopedic surgery?
Non-surgical alternatives include physical therapy, medication (like anti-inflammatories and pain relievers), corticosteroid injections, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, orthobiologics, chiropractic care, bracing or orthotics, and lifestyle modifications such as weight management and exercise.
2. When should I consider alternatives to orthopedic surgery?
Alternatives are often considered when the condition is not severe, or if non-surgical treatments may provide sufficient relief. It’s recommended for patients who wish to avoid surgery or are at higher risk for surgical complications.
3. How can physical therapy help avoid orthopedic surgery?
Physical therapy strengthens muscles, improves joint flexibility, and restores mobility, which can help reduce pain and improve function. It’s often used for conditions like arthritis, tendinitis, and lower back pain to avoid or delay the need for surgery.
4. What are corticosteroid injections, and how do they work?
Corticosteroid injections are anti-inflammatory medications that are injected directly into a joint or injured area. They can relieve pain and inflammation in conditions like arthritis, tendonitis, or bursitis, offering temporary relief without surgery.
5. What is platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy?
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of a patient’s own platelets into an injured area to promote healing. It’s commonly used for tendon injuries, ligament sprains, and osteoarthritis as a non-surgical option.
6. Can medications be an effective alternative to orthopedic surgery?
Yes, medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, or pain relievers can help manage symptoms and improve function in many orthopedic conditions. However, they generally address symptoms rather than the underlying cause.
7. How can weight management help avoid orthopedic surgery?
Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips. Weight loss can reduce pain, improve mobility, and decrease the risk of further joint damage, potentially avoiding the need for surgery.
8. What role does chiropractic care play in treating orthopedic conditions?
Chiropractors use spinal adjustments, manipulations, and manual therapy to relieve pain and improve function in conditions like back pain, neck pain, and joint issues. It can be a non-invasive alternative to surgery, particularly for musculoskeletal misalignments.
9. Are orthobiologics a viable alternative to surgery?
Yes, orthobiologics, such as stem cell therapy or bone marrow aspirate injections, use natural substances to promote healing and tissue regeneration. These treatments are used for cartilage repair, tendon injuries, and early-stage arthritis as an alternative to surgery.
10. When should surgery be considered after trying non-surgical alternatives?
Surgery is considered when non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, or if the condition worsens despite treatment. Surgery may be necessary for severe conditions, such as advanced arthritis, traumatic injuries, or significant joint instability.