Understanding Hip Pain
Hip pain is a common ailment that affects individuals of all ages, significantly impacting their daily lives. The hip joint is a crucial component of the skeletal system, providing stability and mobility. Consequently, when it becomes compromised by pain, it can hinder basic activities such as walking, standing, and even sitting. There are various underlying causes of hip pain, among which arthritis, bursitis, tendinitis, and acute injuries are prevalent.
Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, is one of the leading causes of hip pain in older adults. This degenerative condition results in the degradation of cartilage, leading to friction between bones and consequent pain. Bursitis, characterized by inflammation of the bursa—a small fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between tissues—can also lead to significant discomfort, especially during movement. Similarly, tendinitis occurs when tendons (the fibrous tissue connecting muscles to bones) become inflamed, often as a result of repetitive activities or strain.
In addition to these conditions, acute injuries such as fractures or strains can induce immediate hip pain, often requiring swift medical intervention. Symptoms of hip pain may vary from mild discomfort to severe, persistent pain, often accompanied by stiffness in the joint, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
It is essential for individuals experiencing hip pain to seek accurate diagnosis, as this will inform the most effective non-surgical treatments. Failure to identify the specific cause may lead to inappropriate therapies and prolonged suffering. Tailoring treatment plans to the underlying cause can significantly enhance mobility and overall quality of life. Understanding the complexities of hip pain is the first step toward effective management and recovery.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
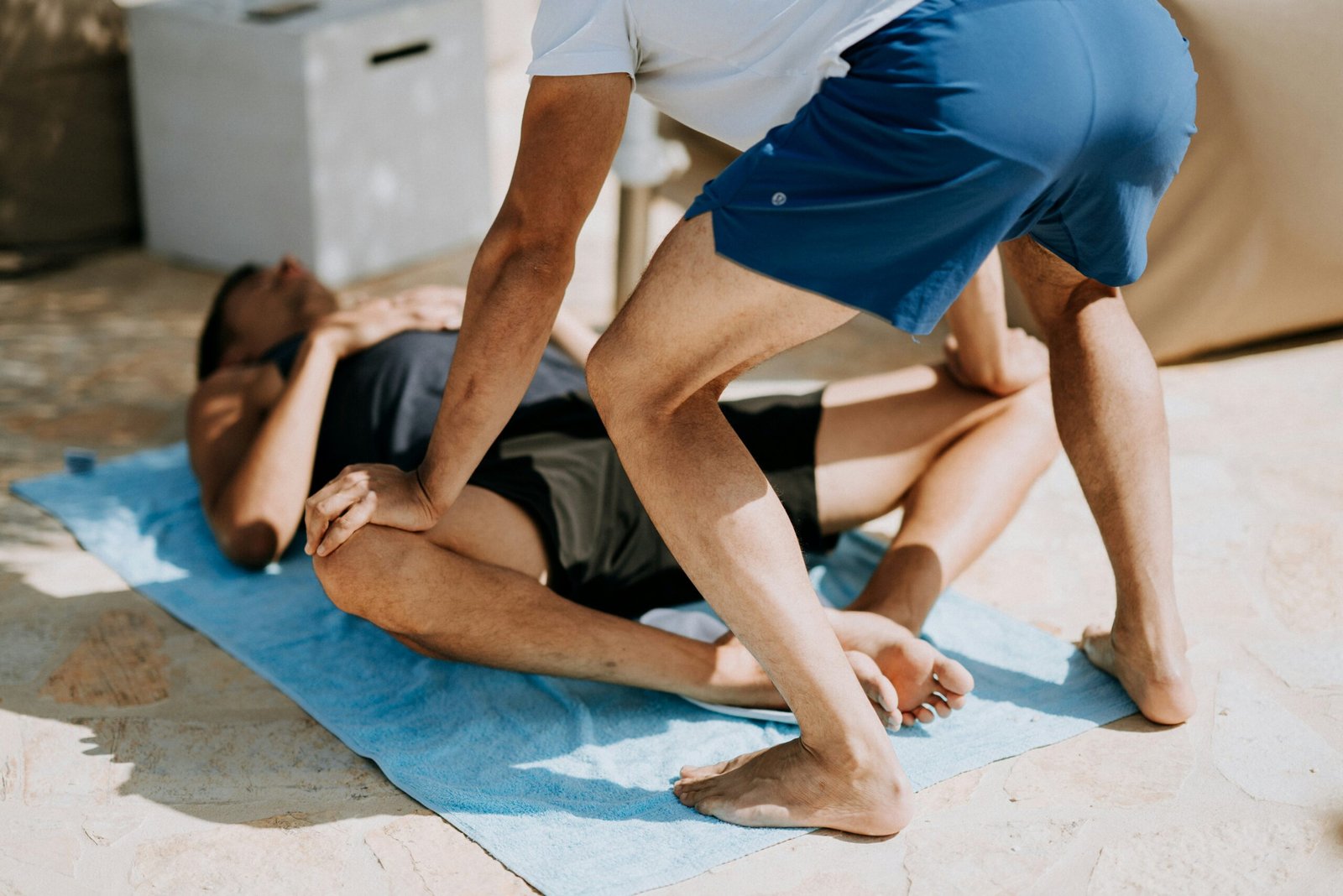
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of hip pain, allowing individuals to regain strength, flexibility, and functionality without the need for invasive interventions. A physical therapist begins by performing a comprehensive assessment to determine the underlying causes of hip discomfort. This assessment includes evaluating the patient’s posture, range of motion, muscle strength, and functional abilities. Based on these findings, therapists can design tailored exercise programs that address the specific needs of each patient, focusing on strengthening the hip muscles and improving overall mobility.
One of the key objectives of a physical therapy program is to strengthen the muscles surrounding the hip joint. Targeted strengthening exercises may involve isometric contractions and resistance training, focusing on the gluteal muscles, quadriceps, and hamstrings. By enhancing the strength of these supporting muscles, patients can better stabilize their hip joint, potentially reducing pain and the risk of injury. Alongside strength training, exercises that enhance flexibility and range of motion are equally important. Stretching exercises can alleviate stiffness and improve mobility, enabling smoother movements and daily activities.
Specific exercises, such as hip abductions, bridges, and clamshells, are commonly incorporated into rehabilitation programs. These movements are essential for strengthening hip stabilizers and improving pelvic alignment. Additionally, therapists may suggest modifications to regular activities, demonstrate proper body mechanics, and advice on ergonomics to minimize hip strain during daily tasks.
Consistency in executing these prescribed exercises is vital for achieving long-term benefits. As patients progress, therapists will gradually adjust the intensity and complexity of the exercises to promote continuous improvement. By adhering to a well-structured exercise regimen and engaging in physical therapy, individuals can significantly reduce hip pain and enhance their overall quality of life.
Medications and Injections
Managing hip pain effectively often involves a combination of medications and injection therapies. For individuals experiencing mild to moderate discomfort, over-the-counter pain relievers are typically the first line of defense. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen work by reducing inflammation, thereby alleviating pain. These medications are readily available and can provide relief for many common issues related to hip pain, such as arthritis or minor injuries.
For more severe or persistent hip pain, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications, including opioids or other analgesics. While these prescription medications can be effective in managing pain, it is crucial for patients to use them under strict medical supervision due to the potential for dependency and other side effects. Adhering to a healthcare provider’s guidelines ensures that these medications are employed safely and effectively.
In addition to medications, injection therapies present viable options for both diagnosis and treatment. Corticosteroid injections are commonly used to reduce inflammation and provide quick pain relief in the hip joint. The anti-inflammatory effects of steroids can result in significant improvement in symptoms for many patients, although the duration of relief may vary.
Hyaluronic acid injections are another alternative, particularly for those with osteoarthritis. By supplementing the natural lubricating fluid in the joints, these injections aim to reduce pain and enhance mobility, offering a potential long-term solution to hip pain. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy uses components from the patient’s own blood to promote healing and regeneration in the affected area. While research into PRP therapy is ongoing, many patients have reported positive outcomes following this treatment.
Each of these medication and injection options carries specific benefits and risks that should be discussed with a healthcare professional. Understanding the nuances of these treatments can lead to a well-informed approach to managing hip pain effectively.
Alternative Treatments and Lifestyle Modifications
Managing hip pain effectively can often involve exploring alternative treatments and making key lifestyle modifications. Among these options, acupuncture has garnered attention for its potential to relieve pain and improve mobility. This ancient practice, rooted in traditional Chinese medicine, aims to restore the body’s energy balance by stimulating specific points with thin needles. A growing body of research suggests that acupuncture may effectively reduce pain in various conditions, including hip pain, by promoting circulation and reducing inflammation.
Chiropractic care is another popular alternative treatment. Chiropractors employ hands-on manipulation techniques to improve spinal alignment and joint function, which can indirectly support hip health. By addressing underlying issues related to the spine and pelvis, chiropractic adjustments may help alleviate pressure on the hip joints and facilitate pain reduction. Numerous patients have reported improved mobility and reduced discomfort following consistent chiropractic sessions.
Massage therapy offers additional benefits for individuals suffering from hip pain. The technique involves manipulating the muscles and soft tissues to relieve tension, increase circulation, and promote relaxation. Therapeutic massage can help address muscle imbalances, alleviate stiffness, and enhance overall joint function, thus providing considerable relief from hip discomfort. Many practitioners tailor sessions to specifically target the affected areas, making it a versatile treatment option.
In addition to alternative therapies, certain lifestyle modifications can complement treatment efforts. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as excess weight places additional strain on the hips. Moreover, adopting a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, may support joint health. Ergonomic adjustments, such as employing proper techniques when lifting or sitting, can further reduce strain on the hips. Collectively, these alternative treatments and lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing hip pain and enhancing overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Question ?
Q. What are the most common causes of hip pain?
Ans. Hip pain can result from conditions like arthritis, bursitis, tendonitis, muscle strains, hip labral tears, or referred pain from the lower back.
Q. What non-surgical treatments are available for hip pain?
Ans. Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, pain-relieving medications, corticosteroid injections, activity modifications, and the use of orthotics or supportive devices.
Q. How does physical therapy help with hip pain?
Ans. Physical therapy strengthens muscles around the hip, improves flexibility, and helps restore joint function, which can reduce pain and prevent future issues.
Q. Can medications relieve hip pain without surgery?
Ans. Yes, over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) or prescribed medications can effectively manage pain and inflammation associated with hip conditions.
Q. What role do corticosteroid injections play in treating hip pain?
Ans. Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide pain relief for several months, especially in cases of arthritis or bursitis, without the need for surgery.
Q. Are lifestyle changes helpful in managing hip pain?
Ans. Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in low-impact exercises (like swimming or cycling), and avoiding activities that aggravate the hip can help alleviate pain and reduce stress on the joint.
Q. Can hip pain improve with rest and activity modifications?
Ans. Yes, modifying activities that cause pain, incorporating rest periods, and adjusting your daily routine can prevent further strain on the hip and support recovery.
Q. Is acupuncture effective for treating hip pain?
Ans. Acupuncture is a non-invasive treatment that can help relieve hip pain by stimulating specific points in the body to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Q. How can I prevent hip pain from recurring?
Ans. Preventing hip pain involves strengthening the muscles around the hip, practicing good posture, maintaining flexibility, and avoiding high-impact activities that could strain the joint.
Q. When should I seek medical advice for hip pain?
Ans. You should consult a doctor if hip pain persists for more than a few weeks, if it’s accompanied by swelling or limited movement, or if it interferes with daily activities despite non-surgical treatments.