Understanding Arthritis and Its Impact on Diet
Arthritis is a term encompassing more than a hundred conditions that result in inflammation and pain in the joints. The most prevalent types of arthritis include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, both of which can significantly affect an individual’s mobility and quality of life. Osteoarthritis, often associated with wear and tear of cartilage over time, tends to manifest as stiffness and pain, particularly after activity. On the other hand, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder whereby the immune system mistakenly attacks joint tissue, leading to severe inflammation and discomfort.
The impact of arthritis extends beyond joint health; it can also affect other areas of physical well-being, making it imperative to address these symptoms proactively. A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing arthritis-related discomfort, as certain foods can either exacerbate inflammation or help mitigate it. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into one’s diet is not merely an adjunct therapy, but rather a fundamental aspect of maintaining overall joint health and improving quality of life. Research indicates that specific dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can be beneficial for individuals suffering from arthritis.
Moreover, certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamin D, have been scientifically linked to reduced symptoms of arthritis. Elements such as these help combat inflammation and bolster joint health. It is essential for those with arthritis to consider their dietary choices carefully, as these can significantly influence inflammation levels and overall joint functionality. The intersection of nutrition and arthritis management highlights the importance of creating a tailored diet plan that addresses individual health needs, setting a foundation for a deeper exploration of specific foods that aid in alleviating joint pain and promoting long-term health.
The Role of Inflammation in Arthritis
Arthritis is a complex condition affecting millions worldwide, characterized by inflammation in the joints. This inflammation can lead to significant pain, swelling, and reduced mobility, ultimately impairing quality of life. At its core, the inflammatory response is a crucial mechanism of the body, designed to protect against infection and facilitate healing. However, when this response becomes chronic, as seen in various types of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, it can contribute to ongoing joint damage and exacerbation of symptoms.
In the context of arthritis, inflammation tends to be a double-edged sword. While it plays a protective role initially, prolonged inflammation can result in the deterioration of cartilage, which serves as a cushion between bones, leading to increased pain and stiffness. Notably, inflammatory markers such as cytokines and C-reactive protein become elevated in individuals suffering from arthritis, signaling the body’s ongoing struggle with inflammation. This persistent inflammation necessitates the incorporation of an anti-inflammatory diet to mitigate symptoms effectively.
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help counteract this ill effect. Foods such as fatty fish, olive oil, nuts, and leafy green vegetables contain various nutrients and compounds that can reduce overall inflammation within the body. These foods not only nourish but also provide antioxidants that may combat oxidative stress, which is often heightened in individuals with arthritis. Incorporating such foods into one’s diet can create an environment less conducive to joint inflammation and pain, enhancing overall joint health.
By understanding the role of inflammation in arthritis, individuals can make informed dietary choices that support their joint health. This knowledge underscores the importance of focusing on nutrition as a fundamental aspect of managing arthritis symptoms, positioning dietary adjustments as a complementary strategy alongside other treatment modalities.
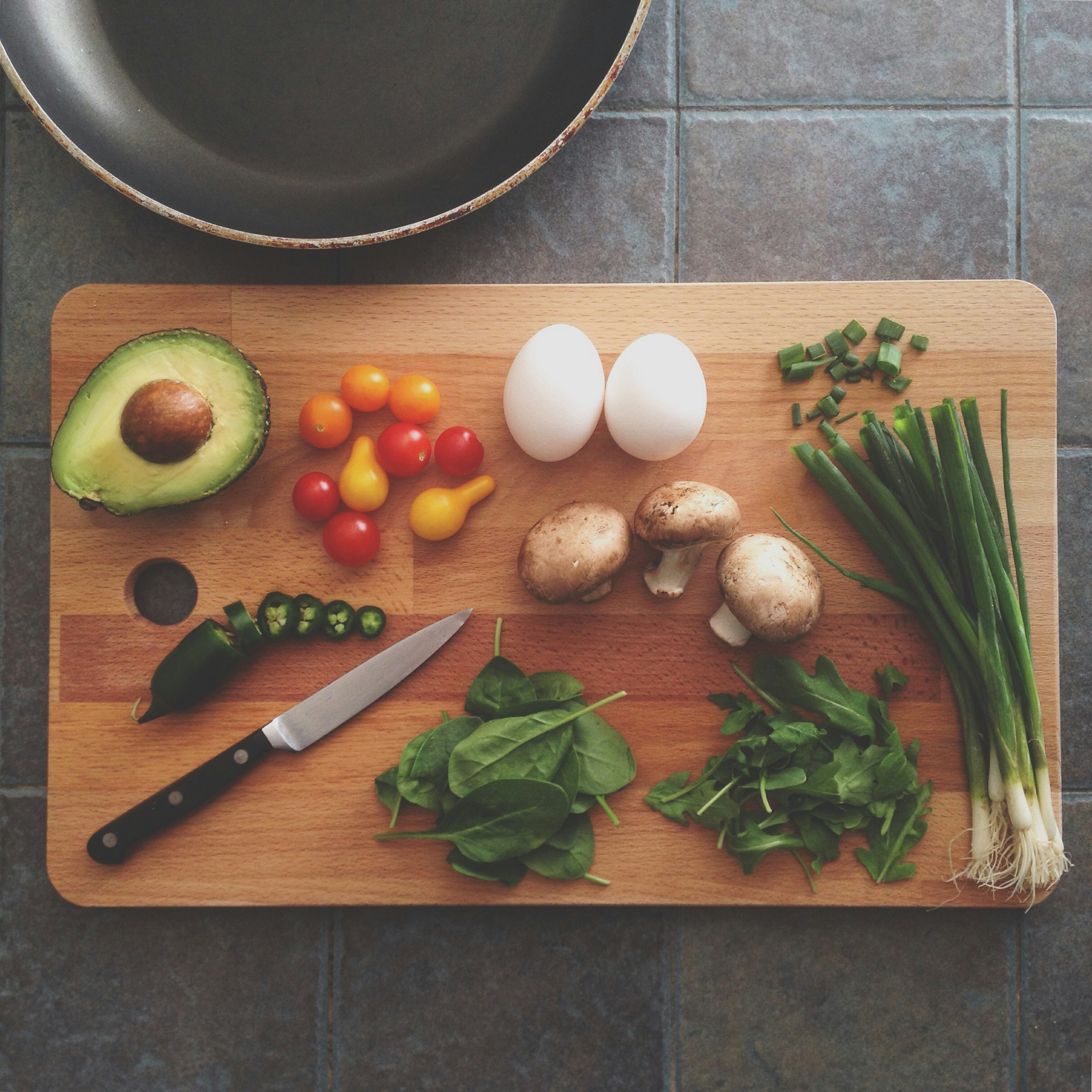
Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods for Joint Health
When considering the management of arthritis, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into one’s diet can play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and promoting joint health. Among the various food options, turmeric stands out due to its active component, curcumin, which possesses significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies suggest that curcumin may inhibit the inflammatory pathway, helping to reduce joint pain and stiffness associated with arthritis. Its vibrant yellow color not only enhances culinary appeal but serves as a natural remedy for inflammation.
Another vital component for joint wellness is omega-3 fatty acids, predominantly found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These polyunsaturated fats are known to lower inflammatory markers in the body. Research indicates that omega-3s can help decrease joint pain and stiffness, making them a beneficial addition for individuals suffering from arthritis. For those who prefer plant-based sources, flaxseeds and walnuts are excellent alternatives, providing similar anti-inflammatory benefits.
Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens also deserve attention in an arthritis-friendly diet. These vegetables are rich in vitamins C and K, both of which are essential for maintaining strong bones and cartilage. The anti-inflammatory compounds present in these greens can support joint health while also contributing to overall well-being. Moreover, incorporating a variety of colored fruits and vegetables, such as berries and cherries, can further enhance this diet by adding antioxidants that fight inflammation.
By carefully selecting anti-inflammatory foods such as turmeric, omega-3-rich fish or flaxseeds, and leafy greens, individuals can create a diet plan that not only helps to alleviate arthritis symptoms but also promotes long-term joint health. Integrating these foods into daily meals can lead to a more nutritionally balanced approach, empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
Foods to Incorporate into Your Arthritis Diet
Individuals dealing with arthritis can significantly benefit from a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods. Incorporating certain fruits and vegetables into daily meals can help alleviate some of the discomfort associated with this condition. For instance, berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries are known for their high levels of antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which have been linked to reducing inflammation in the body. Additionally, leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with vitamins E and C, essential in combating oxidative stress and inflammation, thus promoting joint health.
Nuts and seeds also play a crucial role in the arthritis diet. Walnuts, for example, are an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been demonstrated to help reduce joint stiffness and pain. Similarly, flaxseeds and chia seeds provide rich plant-based omega-3s and help increase fiber intake, which can assist in overall health. Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods can provide substantial benefits for those managing arthritis symptoms.
Whole grains, such as oats, brown rice, and quinoa, should also be included in meals. These grains contain fiber and other nutrients that may assist in reducing inflammation. Whole grains provide essential nutrients that not only help in managing arthritis but also support the overall health of individuals. Moreover, when choosing entrees, opting for lean proteins such as salmon and chicken can also be advantageous due to their lower saturated fat content, contributing further to an anti-inflammatory diet.
Overall, focusing on a well-rounded diet that integrates a variety of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains can enhance joint health. Creating balanced meals incorporating these food options is essential for those looking to effectively manage arthritis symptoms through dietary choices.
Foods to Avoid That Worsen Inflammation
Managing arthritis effectively involves not only incorporating beneficial foods into your diet but also eliminating those that may exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms. Certain dietary choices, especially processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats, have been linked to increased inflammatory responses in the body.
Processed foods are often high in trans fats, preservatives, and artificial ingredients, which can trigger inflammatory pathways. These foods include many fast food items, packaged snacks, and ready-made meals. It is advisable to steer clear of these choices and instead focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that promote joint health. Opting for fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help minimize inflammation.
Refined sugars are another major contributor to inflammation. When consumed in excess, sugars can lead to an imbalance in the body, promoting the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Common sources of refined sugars include sugary beverages, candies, and many breakfast cereals. To reduce your intake, consider replacing these with natural sweeteners, such as honey or fruit, and prioritize unprocessed options that are low in sugar.
Unhealthy fats, particularly omega-6 fatty acids found in certain cooking oils and processed foods, can also lead to increased inflammatory responses. These types of fats often displace healthier fats, like omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for combating inflammation. It is beneficial to replace oils high in omega-6 with those rich in omega-3, such as olive oil or flaxseed oil. Additionally, incorporating fatty fish like salmon into your diet provides essential nutrients that can support joint health.
By being mindful of these common offenders and making healthier choices, individuals with arthritis can help reduce inflammation and potentially alleviate some of the symptoms associated with their condition.
Creating a Balanced Arthritis Diet Plan
Developing a balanced diet plan for arthritis involves incorporating foods that promote joint health while avoiding those that may trigger inflammation. The cornerstone of such a diet is a focus on anti-inflammatory foods, which can help alleviate arthritis symptoms and enhance overall health. To begin, an emphasis should be placed on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
When meal planning, consider using a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables. These foods are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to reduced inflammation. Leafy greens like spinach and kale, alongside berries such as blueberries and strawberries, are particularly beneficial due to their high anti-inflammatory properties. It is advisable to aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables each day, ensuring a range of nutrients.
In terms of protein, incorporating lean sources such as chicken, fish, and legumes is essential. Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, offer additional anti-inflammatory benefits. For those who consume dairy, opting for low-fat or fat-free options can be useful. Moreover, healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts should take center stage in your diet, as they play a crucial role in promoting heart and joint health.
Portion sizes also matter when creating a balanced diet. Consider using smaller plates to help control portions, thus avoiding overeating. Regular meals throughout the day can help maintain energy levels and prevent hunger-driven choices that may include unhealthy snacks. Lastly, staying hydrated is paramount; aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, as proper hydration supports overall well-being and joint function. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet will ultimately aid in managing arthritis symptoms effectively.
Supplements to Consider for Arthritis Relief
Arthritis is a condition that can impair mobility and reduce quality of life. While dietary changes can play a significant role in managing symptoms, certain supplements have gained attention for their potential benefits in arthritis relief. Among these, fish oil omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, and curcumin—derived from turmeric—are closely associated with alleviating discomfort in joints.
Fish oil omega-3 supplements are popular choices due to their anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3 fatty acids are known to reduce inflammation, which can help mitigate joint pain and stiffness. Many studies have suggested that regular intake of omega-3s can lead to significant improvements in arthritis symptoms. However, individuals should consult with healthcare providers before incorporating these supplements, especially if they are on blood-thinning medications, as fish oil can affect clotting.
Glucosamine is another supplement frequently recommended for arthritis relief. It is a naturally occurring compound found in cartilage and is believed to aid in the maintenance and rebuilding of joint tissues. Some research has indicated that glucosamine may help reduce joint pain and enhance mobility in individuals with osteoarthritis. As with other supplements, a discussion with a medical professional is essential prior to starting glucosamine to ensure it aligns with individual health plans.
Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, also shows promise for managing arthritis symptoms. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties have been linked to joint health improvements. Some studies suggest that curcumin can help alleviate pain and swelling in individuals suffering from arthritis. However, because curcumin can have interactions with various medications, consulting a healthcare provider is advisable before incorporating it as a supplement.
Incorporating these supplements into an overall arthritis management strategy, alongside a balanced diet, may offer beneficial effects. Nonetheless, it is crucial to seek personalized recommendations from healthcare professionals to ensure safety and efficacy.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Joint Health
Effective management of arthritis extends beyond dietary choices; it encompasses various lifestyle changes that can significantly enhance joint health. Maintaining an active lifestyle is paramount, as regular physical activity can help reduce stiffness, strengthen muscles around the joints, and improve overall mobility. Engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, or cycling can prove beneficial for individuals facing arthritis. Not only do these activities promote joint function, but they also foster cardiovascular health, which is essential for overall well-being.
Incorporating physical therapy into the arthritis management plan can further assist in maintaining joint health. A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to improve strength and flexibility, aiding individuals in performing daily activities with greater ease. Additionally, physical therapy can teach patients about proper body mechanics, reducing the risk of joint injury during movement and activity.
Stress plays a significant role in the experience of arthritis symptoms; therefore, effective stress management techniques should be part of comprehensive care. Mindfulness practices, meditation, and yoga can help mitigate stress and promote emotional well-being. These techniques encourage relaxation and may lower the perception of pain, further contributing to improved joint health.
Furthermore, ensuring adequate sleep is vital for individuals battling arthritis. Sleep is a crucial time for the body to repair itself, and poor sleep can exacerbate pain and inflammation. Establishing a calming bedtime routine, creating an optimal sleep environment, and addressing any sleep disturbances can positively impact both sleep quality and joint health.
In conclusion, by integrating these essential lifestyle changes alongside a balanced diet, individuals with arthritis can create a multifaceted approach to effectively manage their condition. Fostering an active lifestyle, utilizing physical therapy, managing stress, and prioritizing sleep are all integral components of enhancing joint health and improving the quality of life for those living with arthritis.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals for Personalized Advice
Navigating the complexities of dietary changes, particularly for conditions such as arthritis, necessitates the guidance of healthcare professionals. While general dietary recommendations can provide a foundational understanding, individualized plans are crucial for effective management and symptom relief. Consulting with registered dietitians, nutritionists, or healthcare providers enables patients to tailor their diets based on specific health conditions, preferences, and lifestyles. These professionals can assess one’s nutritional needs in relation to arthritis and recommend foods that may reduce inflammation, promote joint health, and alleviate pain.
Moreover, discussions with healthcare professionals can facilitate the identification of any existing dietary deficiencies or food sensitivities that may exacerbate arthritis symptoms. A personalized nutrition plan allows for the incorporation of anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which can be beneficial for joint health. Additionally, experts can provide essential advice regarding portion sizes and meal timings, ensuring that the diet is balanced and sustainable long-term.
Another critical aspect to consider is the potential interaction between specific foods and medications used to treat arthritis. Certain foods may enhance the efficacy of medications, while others could interfere with them. This highlights the importance of a well-informed approach when integrating new foods into one’s diet. Healthcare professionals can provide this insight, helping to mitigate risks associated with dietary changes and medication interactions. Therefore, seeking expert advice ensures that dietary adjustments not only align with individual health goals but also support holistic well-being.
In conclusion, working alongside healthcare professionals to develop a personalized plan is an essential step in managing arthritis through diet. Their expertise can empower individuals to make informed choices that promote joint health and enhance overall quality of life.