Understanding Augmented Reality and Its Application in Surgery
Augmented Reality (AR) is a cutting-edge technology that enhances the real-world environment by superimposing digital information onto it. Unlike virtual reality, which creates a completely immersive experience in a computer-generated environment, AR enriches the existing environment with relevant data, thereby providing a unique overlay of information that can be utilized in several fields, particularly in medicine and surgery.
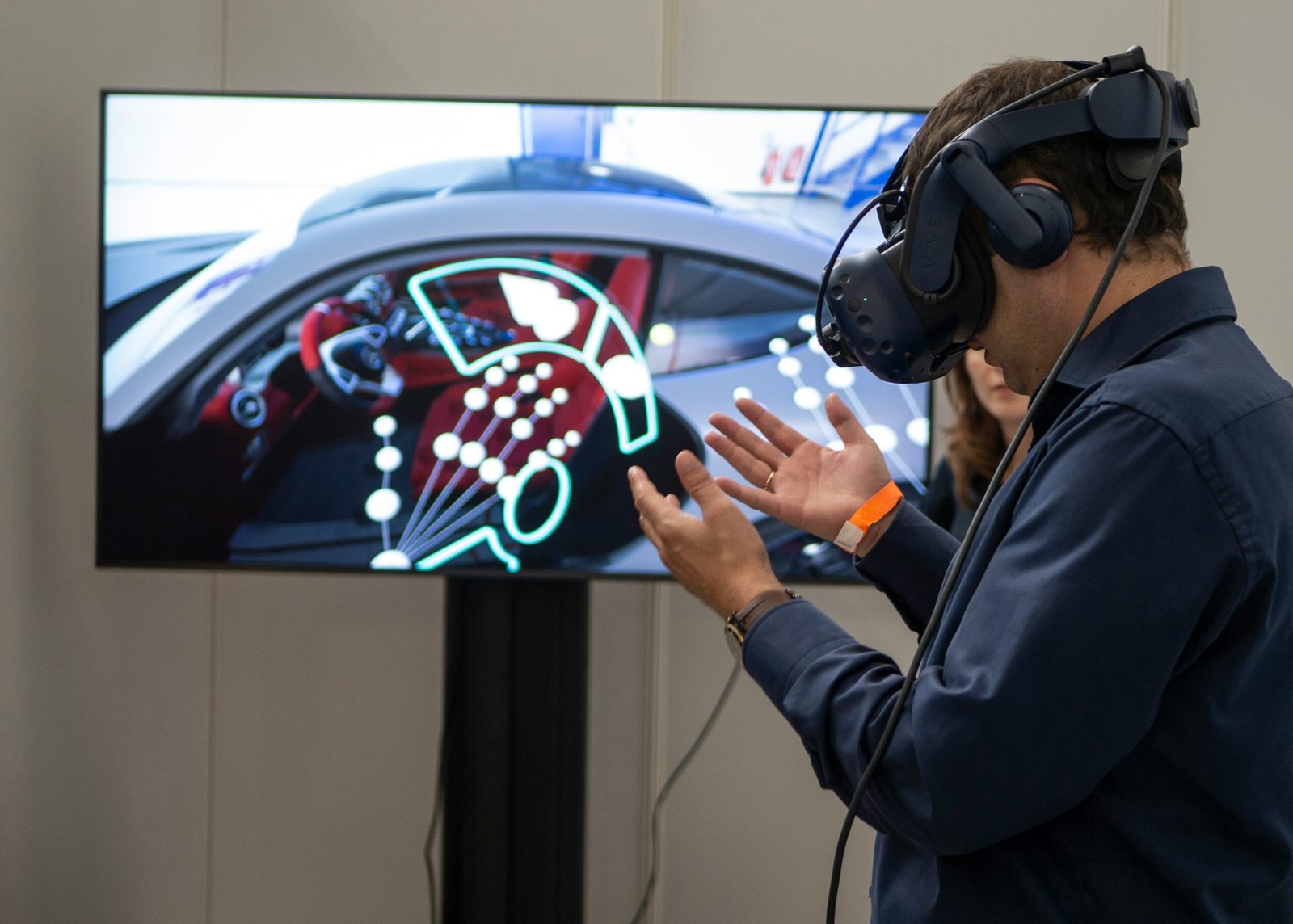
The fundamental principles behind AR involve the integration of digital elements—such as images, sounds, and other data—into a person’s view of the real world. In the surgical context, this technology enables surgeons to visualize critical information, such as patient anatomy, in real time during procedures. This combination of real and virtual imagery enhances the surgeon’s capabilities, allowing for improved precision and accuracy in complex operations.
Several AR tools have been developed specifically for surgical applications, including AR glasses and software applications tailored for surgical environments. AR glasses, for instance, provide a hands-free display of essential information, such as anatomical models or patient data, directly in the surgeon’s line of sight. This allows for seamless integration of digital overlays into the surgical field, ensuring that critical data is always available without the need to divert attention away from the procedure.
Moreover, AR is particularly valuable in visualizing unexposed bones and tissues. By providing intricate details about structures that are not immediately visible to the naked eye, AR significantly enhances the surgeon’s understanding of the surgical landscape. The enhanced visualization capabilities not only boost confidence among surgeons but also contribute to better patient outcomes through minimized complications and improved surgical precision.
Benefits of Augmented Reality for Surgeons
Augmented Reality (AR) is significantly transforming the landscape of surgery by providing surgeons with innovative tools that enhance their capabilities. One of the primary advantages of AR is the enhanced visualization of anatomical structures. Surgeons can overlay critical imaging data, such as CT scans and MRIs, onto the patient’s body in real time. This capability enables them to visualize complex anatomical details more clearly, reducing the chances of overlooking important structures during surgical procedures. By providing a three-dimensional perspective, AR aids surgeons in navigating intricate anatomy, ultimately leading to more precise interventions.
Moreover, the increased accuracy in surgical procedures facilitated by AR cannot be overstated. Through the integration of spatial data, surgeons can accurately pinpoint where incisions should be made, significantly improving the outcome and efficiency of the procedure. The combination of real-time data and visual aids ensures that surgeons can make informed decisions, mitigating risks associated with traditional surgical methods. Research has indicated that the use of AR in surgery not only enhances precision but also decreases operation time and minimizes postoperative complications.
Another significant benefit of AR pertains to improved preoperative planning. Surgeons can simulate surgeries before actual procedures, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the case. This level of preparation ensures that the surgical team is well-acquainted with the patient’s unique anatomy and the specific challenges they may encounter during the operation. Additionally, AR can greatly reduce the learning curve for new surgeons. By utilizing AR systems that provide real-time guidance and feedback during surgery, novice surgeons can gain valuable insights and improve their skills in a controlled environment.
Several case studies underscore the positive impact of AR on surgical outcomes. For instance, cases involving minimally invasive surgeries have demonstrated higher success rates and improved patient recovery times when AR technologies were employed. As AR continues to evolve, its application in surgery promises to enhance surgical precision and outcomes significantly, making it an invaluable asset in the healthcare field.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Augmented Reality in Surgery
The integration of augmented reality (AR) technology in surgery presents numerous challenges and limitations that must be thoroughly navigated. One of the most significant barriers is the high cost associated with AR systems. Developing and implementing advanced AR technologies often require substantial financial investment, which can be prohibitive for many medical institutions. These costs encompass not only the hardware and software necessary for AR functionality but also maintenance, updates, and potential repairs, placing a strain on healthcare budgets.
Another notable challenge is the necessity for extensive training among surgical staff. Surgeons and the operating room team must become proficient in utilizing AR tools to harness their full potential effectively. This need for specialized training can divert time and resources away from regular surgical procedures, potentially slowing down the overall efficiency of a surgical department. Moreover, ensuring that surgical staff is adequately trained on the operation of AR systems is imperative to minimize the risks of errors during surgery.
Ethical considerations cannot be overlooked, as the use of AR in surgery raises questions about patient safety, privacy, and informed consent. Surgeons must ensure that patients are adequately informed about the role of AR in their procedures, maintaining transparency and fostering trust. As medical institutions explore the promise of augmented reality, understanding these challenges will be vital to adopting safe, effective, and ethically sound AR systems while maximizing their benefits in surgical settings.
The Future of Augmented Reality in Surgery
As the field of surgery continues to evolve, augmented reality (AR) is poised to significantly enhance surgical precision and overall patient outcomes. With ongoing advancements in technology, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities stands out as a pivotal trend. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, enabling surgeons to make informed, real-time decisions based on patient-specific information. For instance, AI systems could assist in the identification of anatomical structures, minimizing the risk of complications during complex procedures.
Moreover, improvements in AR hardware are set to transform the surgical landscape. Devices such as smart glasses and head-mounted displays are becoming more sophisticated and accessible, allowing for seamless overlay of digital information onto the surgeon’s physical field of view. This could lead to enhanced visualization of critical structures, ultimately improving the accuracy of surgical interventions. Such advancements may also enable more effective training simulations for medical students and residents, recreating high-fidelity surgical scenarios that mimic real-world conditions.
The wider adoption of AR technologies in medical education is another promising direction. By providing immersive training experiences, future surgeons can develop their skills in a controlled environment, reducing the learning curve associated with complex procedures. This could potentially lead to a new generation of surgeons who are better prepared for the challenges of modern surgical practice, thus enhancing overall surgical proficiency.
In conclusion, the future of augmented reality in surgery appears bright, with the potential to reshape the approaches taken in both surgical practices and medical education. As these technologies continue to develop, they can help create a more informed and capable surgical community, ultimately benefiting patients through improved surgical techniques and outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions?
Q. How does augmented reality (AR) help surgeons visualize unexposed bones and tissues during surgery?
Ans. AR overlays 3D images of bones and tissues onto the surgical site, allowing surgeons to “see” structures hidden beneath the surface without additional incisions.
Q. What types of surgeries can benefit from the use of AR technology?
Ans. AR is particularly beneficial in orthopedic, neurosurgical, and minimally invasive procedures where precise visualization of complex anatomical structures is essential.
Q. Is augmented reality (AR) safe to use in complex surgical procedures?
Ans. Yes, AR is designed to enhance accuracy and precision, and studies suggest that it can improve surgical outcomes by providing real-time, accurate information during procedures.
Q. How accurate is AR technology in guiding surgeons during operations?
Ans. AR systems are highly accurate, often integrated with imaging technologies like MRI or CT scans, allowing surgeons to navigate within millimeter precision.
Q. What equipment is required to implement AR in the operating room?
Ans. AR setups typically include specialized headsets or glasses, a 3D imaging system (such as CT or MRI), and software that integrates real-time data for visualization.
Q. How does AR compare to traditional imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans during surgery?
Ans. Unlike static images from X-rays or CT scans, AR provides dynamic, real-time overlays directly onto the surgical field, offering better spatial awareness and minimizing the need for repeated imaging.
Q. Does using AR technology reduce the risk of complications during surgery?
Ans. Yes, by improving visualization and precision, AR can reduce the risk of damage to surrounding tissues, nerves, and blood vessels, thereby minimizing complications.
Q. Can augmented reality (AR) shorten the duration of surgeries?
Ans. Yes, AR can streamline surgical procedures by providing critical information more quickly, allowing surgeons to perform tasks with greater efficiency and precision, which can reduce operating times.
Q. How does AR impact surgical training and education for medical professionals?
Ans. AR offers an immersive training environment, allowing surgeons to practice complex procedures in virtual simulations before performing them in real life, enhancing their skill and confidence.
Q. What are the potential limitations or challenges in using augmented reality in surgery?
Ans. The main challenges include the high cost of AR systems, the need for specialized training, and potential technical limitations in certain complex surgeries where real-time data processing may still face delays.